Group Final Presentation - CALtea
Saturday, December 8, 2012
Wednesday, December 5, 2012
Group Final Project - Requirements:
Group projects of Team Base Conference and Fall 2012 Semester group Final Project
Group projects of Team Base Conference and Fall 2012 Semester group Final Project
Group members: Stephen Shiao, Virginia Atkinson, Darren Tay, Pei Pei Li
Date of discuss: 11/29/2012
Thank you all for attended our group Skype discussion!
After half an hour reviewing on the event, we moved to our next topic of the fall 2012 semester final projet.
Final Presentation (Team based, Dec 8, 9:30-11:00AM)
An Innovative Start-up Business
Goals: Make it interesting and attractive so
A. people want to invest in your business.
B. people want to join your team.
Requirement:
10-12 min, every member has to present
Well structured and design powerpoint 8-15 pages
Use at least 5 concepts and 10 "takeaways terms" in the book, list them at the last slide)
Include 3 min of "Porter's 5 forces analysis" of the industry your start-up will be in.
Make it fun!
We separated this final project into parts, and each of group member will handle each selected parts before the next Tuesday, 4 December. We looking forward to finish the final adjusting of our project no later than next Friday, 7 December.
Stephen selected parts of "Operations" and "MBA Minicourses";
Darren selected "Economics" and "Strategy";
Pei Pei selected "Accounting" and "Finance";
Virginia selected "Marketing" and "Ethic".
Each one 3 slides with 1 concept, and 2 take away.
After brainstorm around several industries such as boba pearl tea, fashion store, dry clean shop, swimming school and mailing company/forwarding agent, we voted to involving in boba pearl tea business as our final presentation topic. And this tea shop will be named as CalTea
Porter’s 5 forces Analysis:
page 340
Stephen/entrants
Darren/buyer/rivalry
Peipei/supplier
Viginia/substitute
Group Study Report - Country Analysis:
Analysis Past performance
External
Internal
Strategy
Goal
Policy
Context,
physical - size, resources, imports/exports
Institution - industrial, infrastructural, bureaucracy
Ideological - bill of rights, culture, immigration, material wealth
Prediction
Outlook for 2012-2017
Conclusion:
Country Analysis: Do you want to setup your company here?
Date: 10 November - 16 November 2012
Group Member: Stephen Shiao, Virginia Atkinson, Darren
Tay, Peipei Li
Subject Country: Malaysia:
Topics:
- Analysis
Past performance
- External
- Internal
- Strategy
- Goal
- Policy
- Context,
- physical
- size, resources, imports/exports
- political
- stable,democracy, power, government, corruption, vigilant press
- Institution
- industrial, infrastructural, bureaucracy
- Ideological
- bill of rihts, culture, immigration, material wealth
- International
- inflation
- prediction
Analysis Past performance
External
In 2012, Malaysia hosted the
world's second-largest initial public offering (IPO) when a local palm oil
producer, Felda Global Ventures, listed on the local stock market, Bursa
Malaysia, on June 28th.
•The IPO is part of a
government plan to sell off state-linked firms and attract foreign investors to
the country. This initiative forms one element of a plan to transform Malaysia
into a high-income nation by 2020.
Internal
Recent statements by the
prime minister, Najib Razak, and his deputy, Muhyiddin Yassin, have hinted that
more cash hand-outs could be in the offing as speculation persists over a
possible snap election later this year.
Strategy
Goal
Services in Malaysia have
been growing in importance for the economy in the past few years. In 2010,
Services was responsible for 49.3 percent of the GDP. The concerted development
of the service industry is part of the national development strategy to venture
into new growth areas and broaden the economic base for exports. It is also
expected to provide the basis for sustained growth in the economy in order to
achieve the vision of becoming a developed nation by 2020.
According to the 10th
Malaysia Plan (RMK 10), the goal for the service industry is to achieve 61
percent of GDP share by 2015 – with an annual growth of 7.2 percent. Under the
IMP3, non-government services are targeted to grow at an average annual rate of
7.5 percent. Construction services are also expected to increase annually by
5.7 percent. The Malaysia government is also expected to invest nearly RM687.7
billion or US$228.384 billion dollars over the next fifteen years into services
alone.
Policy
The monetary policy
committee of Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM, the central bank) kept its official
policy interest rate, the overnight policy rate, unchanged at 3% at its meeting
in July 2012.
Context,
physical - size, resources, imports/exports
The strength of domestic
demand was borne out in trade data for May, which showed a 16.2% year-on-year
jump in the value of imports. This, coupled with other data, has prompted an
upward revision to our GDP forecast for 2012.
political - stable, democracy,
power, government, corruption, vigilant press
Institution - industrial, infrastructural, bureaucracy
Malaysia is a newly
industrialized country that experienced an economic boom and underwent rapid
development during the late 20th century. Prior to this rapid of rapid
industrialization, Malaysia was the world’s largest producer of tin, rubber and
palm oil. When the tin market collapsed during the early 1980s, the Malaysian
government was forced to diversify and modernize the economy.
Today, Malaysia has moved
into the third stage of economic development, with growing emphasis on
services. The Industrial Master Plan (IMP3) was created to develop the country
into a major trading nation by focusing on services and human capital. IMP3 is
expected to cover the period from 2006 to 2020.
Malaysia also has a vibrant
oil and gas industry. In 2010, Malaysia was the 28th largest oil producer and
the 17th largest natural gas producer in the world. Currently, Malaysia has 2.9
billion barrels worth of proven oil reserves and 2.35 trillion cu m of proven
natural gas reserves. This makes them the 32nd and 17th ranked country in the
world respectively.
Oil and natural gas reserves
in Malaysia are managed by Petronas – a Fortune 500 company wholly owned by the
Malaysian government.
Ideological - bill of rights, culture, immigration, material wealth
International – inflation
Expect consumer prices to
rise by an average of 1.9% in 2012, compared with 2.2% previously. Annual
inflation will average 3% in 2013-16. The planned introduction of a new
consumption tax and the gradual withdrawal of subsidies are expected to push up
consumer prices from 2013.
During the first eight
months of the year the overall consumer price index rose by an average of 1.8%
year on year. The food and non-alcoholic beverages category recorded a 2.8%
year-on-year increase in prices
Prediction
Outlook for 2012-2017
•The forecast period is
likely to be dominated by preparations for the next general election. The poll
does not have to take place until 2013, but the Economist Intelligence Unit
expects it to be held in 2012.
•We expect the ruling
Barisan Nasional (BN) coalition to win the next election. The BN hopes to
regain the two-thirds majority that it lost at the 2008 general election.
• The government will fail
to balance the budget in 2013-17 as it continues to allocate funds to
infrastructure projects. The monetary authorities will maintain a neutral
stance in 2013, but will tighten policy from 2014 onwards.
• The economy is expected to
remain on a sustainable growth path in 2013-17. Growth in 2013 is expected to
slow slightly to 4.5%, compared with an estimated 4.9% in 2012.
• The current account will
remain in surplus in 2013-17, equivalent to an annual average of 6.2% of GDP,
compared with an estimated 6.7% in 2012.
Conclusion:
We have more than 50% vote
among team members favors forming investment in Malaysia. Followings are the
summary of our discussion result, leads us believe it will be profitable to
start business in there.
Malaysia will continue to
post substantial trade and current-account surpluses in the next five years.
The service industry is important, e.g. data center etc. It is one of the five
countries without debt in South Asia, The political dominate and controls the
economy, it’s all about relationship, which leads corruption. Race is one of
the big problems.
The North east beach is
white sand beach, better than Hawaii. It is good for tourist business
development.
Land and Real Estate was
gaining 30-40 % but now is decline. Tourist and sightseeing are good business, good
for put money opening shops. Malaysia ranks 9th place for retirement
in the world. Some hi-tech industry formed some base here; for example, it is
the first setup of out of state factory for Intel. It has 2nd/3rd biggest IPO
in 2012.
There are 60 % of the
surface is open for land development, very rich in nature resources. Food and
water are very good, which supplies surrounding countries. General election
date is decided by Prime Minister. It supposes to take place in 2012, but
becomes to be expected 2013.
BN to Malaysia is similar to Democratic Party to US.
There are some small ones but no effect to the control of the country. Muslin
and DAP have few seats in the congress.
Small has been grouped into
UMNO, which one of the three to form BN. People are Malaysian, Indian and
Chinese, and populations are biased. The combination of different people forms
different parties.
Land and factory building in
china is good experience for industry development. Base on this, does Malaysia
will be next wave? The answer is positive.
Business formed alliance of
several small countries, they are helping each other and form attractive
investment environment, and put Singapore as its center, also balanced each
other. Malaysia has bright future and worth to put money for business
development.
Group Project:Team based Conference/Event experience:

Our team objective was to learn what we could from the event held jointly by these two companies of the advanced storage technology in the public cloud field. It is also a good practise not only to know the latest technology in the industry, but also enhance our knowledge to learn about how the event being planned and organized, in the supplier side, and what’s being delivered, in the customer side. Our collaboration was in class and on the Internet to discuss the activity we were going to participate in as a group. Also we had meetings online to discuss the conference after we attended it, came together at the conference to listen to the presentation from Nimble and CommVault representatives. We also collaborated on the written assignment.
Nimble Storage is the first purpose-built storage solution that combines flash memory with hard disk drives to deliver high performance and efficiency. You can consolidate and better protect data while reducing overall storage costs for all your critical IT applications using Nibble’s easy-to-manage, scale-to-fit storage.
CommVault customers can now realize these breakthroughs with support for Nimble Storage as a Qualified IntelliSnapTM Connect array. Efficiently capture, move, retain, find, analyze, and recover data with an efficient, high-performance storage solution. A cooperative support agreement between Nimble Storage and CommVault® software ensures seamless compatibility and customer support.
With the combination of the above 2 companies, the storage subsystem for the cloud implementation can be more efficient, sufficient and complete.
The two companies exchanged information, shared a video, and had a PowerPoint presentation. The advantage of the technology and price has been mentioned. In addition they had a question and answer period where many questions were well answered. When the two speakers we done they said that there was a short survey they were handing out to obtain feedback from customers. To encourage questions and people to fill out the survey they had prizes such as tickets for movies and snacks at the concession stand.
Few days later, all of the group members received a phone call from the event as followup from the sales and marketing department of those two companies.
This also let us review the product, the offered price, with the proper channel of promotion their product at the matched place of center of Silicon Valeey.
After a detailed group discussion we got a better understanding of the purpose of the event.
Group Project
Team based Conference/Event experience
BUS 600-FA 2012
Graduate Prosem - Fundamentals of Management
Stephen Shiao
Virginia Atkinson
Peipei Li
Darren Tay
Dec 02, 2012
California University of Management and Technology
Instructor: Professor Eric Tao
Group Project
Team based Conference/Event experience
Collaboration and Objectives
Our Group went a to a Nimble and CommVault Product Announcement Event. Upon completion of speech of technology and product introduction from these two companies, they showed the latest movie Skyfall - 007, filmed with updated cloud technologies.Our team objective was to learn what we could from the event held jointly by these two companies of the advanced storage technology in the public cloud field. It is also a good practise not only to know the latest technology in the industry, but also enhance our knowledge to learn about how the event being planned and organized, in the supplier side, and what’s being delivered, in the customer side. Our collaboration was in class and on the Internet to discuss the activity we were going to participate in as a group. Also we had meetings online to discuss the conference after we attended it, came together at the conference to listen to the presentation from Nimble and CommVault representatives. We also collaborated on the written assignment.
Background on two companies
Cloud is the latest technology to handle the “Big Data” era, storage system plays an important role. The storage size, security, efficiency, bandwidth, access speed, data management, backup, real estate/rack space, power, safety, support and availability are few examples of important factors among others in the data center setup and management for the storages.Nimble Storage is the first purpose-built storage solution that combines flash memory with hard disk drives to deliver high performance and efficiency. You can consolidate and better protect data while reducing overall storage costs for all your critical IT applications using Nibble’s easy-to-manage, scale-to-fit storage.
CommVault customers can now realize these breakthroughs with support for Nimble Storage as a Qualified IntelliSnapTM Connect array. Efficiently capture, move, retain, find, analyze, and recover data with an efficient, high-performance storage solution. A cooperative support agreement between Nimble Storage and CommVault® software ensures seamless compatibility and customer support.
With the combination of the above 2 companies, the storage subsystem for the cloud implementation can be more efficient, sufficient and complete.
The Six W’s
People who worked as IT professionals and management area should attend this presentation. It was taken place at a movie theater called AMC Mercado in Santa Clara, CA on November 9th 2012.The two companies exchanged information, shared a video, and had a PowerPoint presentation. The advantage of the technology and price has been mentioned. In addition they had a question and answer period where many questions were well answered. When the two speakers we done they said that there was a short survey they were handing out to obtain feedback from customers. To encourage questions and people to fill out the survey they had prizes such as tickets for movies and snacks at the concession stand.
Few days later, all of the group members received a phone call from the event as followup from the sales and marketing department of those two companies.
What did we learn from the event?
What we learned from the event was that companies are providing solutions with hard drive for store, backup and management of storage subsystems for the data center in the cloud industry. Also, this is an efficient way of inviting specific group of professionals with adequate background in the specific segment of the market, position their product in the specific field, focus on educating customer with latest information and differentiate from the rest of the other suppliers.This also let us review the product, the offered price, with the proper channel of promotion their product at the matched place of center of Silicon Valeey.
After a detailed group discussion we got a better understanding of the purpose of the event.
Wednesday, November 28, 2012
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 10 - Mini Courses
MBA Minicourses
I will list out the concepts I learned from Chapter 10.
MBA Minicourses
I will list out the concepts I learned from Chapter 10.
- Ten-second minicourse on public speaking:
- Know your audience
- Their interests, attention span
- Know your own capabilities
- Can you deliver a joke?
- Keep it simple
- detailed information is best delivered in print
- Speeches should deliver a concept and motivate
- KISS
- Keep It Short & Simple
Saturday, November 17, 2012
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 9 - Strategy
Porter's Five Force
Inbound Logistics: Vendors selection, net payment term, Shipping method
Operations - employee has the right skill, quality control, training
Outbound Logistics - how do you sell, lead time, delivery
Marketing & Sales
Services
Level of Strategy
Functional Strategy: Can we improve how to do operation?
Business Strategy: How can we beat the competition?
Corporate Strategy: What business should we be in?
Porter's Five Force
According to Harvard
professor Michael Porter, an industry can be analyzed using a Five-Forces
Model. These forces determine how intense competition is within a particular
industry. Industries with low intensity, are considered attractive, as they are
profitable.
Value Chain - important analysis toolInbound Logistics: Vendors selection, net payment term, Shipping method
Operations - employee has the right skill, quality control, training
Outbound Logistics - how do you sell, lead time, delivery
Marketing & Sales
Services
Level of Strategy
Functional Strategy: Can we improve how to do operation?
Business Strategy: How can we beat the competition?
Corporate Strategy: What business should we be in?
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 8 - Economics
Below is a couple useful concepts I learned in the economics chapter.
Some economists like to break down opportunity costs into explicit and implicit. An explicit opportunity cost involves cash outlays. An implicit opportunity cost is one that involves what you could have done with resources you already own.
Below is a couple useful concepts I learned in the economics chapter.
- Supply and Demand
- Opportunity Costs - Opportunity cost is the cost we pay when we give up something to get something else.
Some economists like to break down opportunity costs into explicit and implicit. An explicit opportunity cost involves cash outlays. An implicit opportunity cost is one that involves what you could have done with resources you already own.
- Marginal Utility
- Elasticity
- Market Structures
- Keynesian and Monetarist Thery
- Gross National Product Accounting
- International Economics
Saturday, November 3, 2012
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 7 - Operations
I pick up a couple concepts related to Operations below.
* Machines
* Methods
* Materials
* Messages
* Money
* Manpower (People)
2. Critical Path method (CPM) - Sophisticated scheduling method for projects
Critical path is the path of critical activities, i.e. activity which has slack/float 0 or less than 0. In this example, the critical path is Activity 1, Activity 2 and Activity 5. Delay should be avoided in these activities, since it will cause delay in overall project completion. Activities 3 and 4 are more flexible, nevertheless project stakeholder should pay attention to the latet finish of these activities to avoid preasure to next critical activity, Activity 5
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 6 - Finance
I pick up a couple concepts related to Finance below.
1. Risk and Return
Discounted Cash Flow
I pick up a couple concepts related to Operations below.
- Six M's of Capacity
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
* Machines
* Methods
* Materials
* Messages
* Money
* Manpower (People)
2. Critical Path method (CPM) - Sophisticated scheduling method for projects
Critical path is the path of critical activities, i.e. activity which has slack/float 0 or less than 0. In this example, the critical path is Activity 1, Activity 2 and Activity 5. Delay should be avoided in these activities, since it will cause delay in overall project completion. Activities 3 and 4 are more flexible, nevertheless project stakeholder should pay attention to the latet finish of these activities to avoid preasure to next critical activity, Activity 5
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 6 - Finance
I pick up a couple concepts related to Finance below.
- Capital Structure
- Discounted Cash Flow
1. Risk and Return
- The relationship between risk and return is one of the fundamental relationship in finance, because investors are risk averse, meaning they prefer less risk to greater risk.
- Investors who are risk averse will not invest in risky securities without greater expected returns.It means that to earn greater expected returns investors must be willing to accept greater risk.
- Investors typically hold a collection or portfolio of assets, we need examine the risk of the portfolion context
- Risk and return in a portfolio is very different from stand-alone risk and return due to diversification effects.
- First examine the return of portfolio, then consider the risk of a portfolio
- The measure of risk most commonly used in the single-factor CAPM is called beta (β).
- Cost of Capital
- Capital includes funds supplied to the firm by long-term investors.
- These are usually stockholders and bondholders.
- The cost of debt is the interest rate the firm would pay if it issued new debt today.
- Usually the firm will pay about the market interest rate (yield to maturity) on its bonds.
Discounted Cash Flow
- Financial assets are substitutes for each other.
- That implies that they have some properties in common, but will be differentiated in other dimensions
- A substantial piece of this course is learning how to use Excel.
- Use Excel for basic arithmetic operations:
+, -, *, / (with occasional SUM()). - This chapter makes heavy use of many Excel functions.
- Time Value of Money
- If I owe you a sum of money, would you rather receive it today or a year from today? The time value of money refers to wht the value of a dollar amount is today (present value) versus what the value of that same dollar amount will be in X amount of time (future value)
- Future Value
- The future value (FV) of this security is its value after a specified time has passed
- In this case the future value is $100+(0.05)($100)=$105.
- Present Value
- The future value of any sum today is FV = PV x (1 + I)N. That means PV = FV/(1 + I)N
- What is the amount that we need to invest or deposit today in order to have a specific amount in the future?
- Annuities
- Annuities meet three criteria:
- Pay an equal amount
- At a specific time interval
- For a specific time period
- Annuities meet three criteria:
Friday, October 26, 2012
STOCK PICK: Nvidia

9:46:20 PM] Stephen Shiao: Price: dropped 20% in past 2 months, but forecast is bullish at Q2 earning (in August). Q4 expected $1.01~$1.26B. Current at 5% of 52 week low.
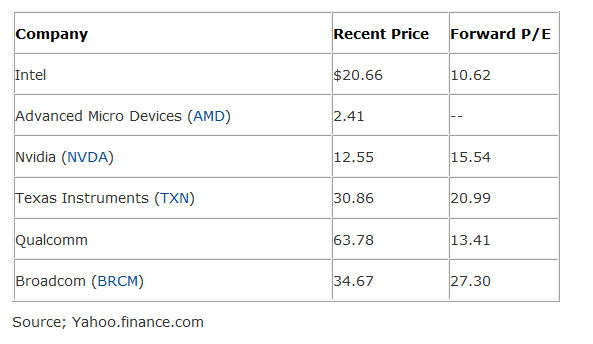 |

9:46:20 PM] Stephen Shiao: Price: dropped 20% in past 2 months, but forecast is bullish at Q2 earning (in August). Q4 expected $1.01~$1.26B. Current at 5% of 52 week low.
[9:47:19 PM] Stephen Shiao: Apple: 15" iMac (4-5M units/yr) come with Kepler line of GPU.
[9:48:29 PM] Stephen Shiao: Mobile/Tablet: Tega 3 SoC powered Google Nexus 7, Amazon Kindle File + HD, Segment as low end priced ($199 ~ $249), because Apple iPad-Mini priced $329
[9:50:33 PM] Stephen Shiao: PC: HP/DELL will follow Apple use GeForce
[9:51:19 PM] Stephen Shiao: Game: GeForce, 60% faster.
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 5 - Quantitative Analysis
I learned a couple concepts in Quantitative Analysis
2. Sunk Cost:
What is a "sunk cost"? What is the definition of a "sunk cost"? What does the term "sunk cost" mean?
"Sunk cost" is a business term that refers to a cost that has been spent and can not be recovered.
Example 1: A company decides to spend $30,000,000 building a new warehouse.
After spending $15 million on the construction of the newA warehouse, with similar specs to the one that the company is currently building, is listed at a price of $10 million.
The company has "sunk costs" of $15 million (this amount can't be recovered, as the new warehouse is incomplete and can't be sold).
From an economic standpoint, the smart decision would be for the company to abandon the construction of their new warehouse and buy the one that is being listed for $10 million.
However, sunk costs usually incur a form of "emotional investment", and many people have a hard time walking away from something once they have incurred costs that can not be recovered. warehouse, the real estate market in the area begins to tank due to a very weak economy.
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 4 - Organizational Behavior

The following tree structures illustrated how a large organizational behavior.
I learned a couple concepts in Quantitative Analysis
- Decision Trees - A way to graphically show and quantify multiple outcomes of a business decision
- Sunk Cost - Investment made in the past that have no bearing on future investment decisions
2. Sunk Cost:
What is a "sunk cost"? What is the definition of a "sunk cost"? What does the term "sunk cost" mean?
"Sunk cost" is a business term that refers to a cost that has been spent and can not be recovered.
Example 1: A company decides to spend $30,000,000 building a new warehouse.
After spending $15 million on the construction of the newA warehouse, with similar specs to the one that the company is currently building, is listed at a price of $10 million.
The company has "sunk costs" of $15 million (this amount can't be recovered, as the new warehouse is incomplete and can't be sold).
From an economic standpoint, the smart decision would be for the company to abandon the construction of their new warehouse and buy the one that is being listed for $10 million.
However, sunk costs usually incur a form of "emotional investment", and many people have a hard time walking away from something once they have incurred costs that can not be recovered. warehouse, the real estate market in the area begins to tank due to a very weak economy.
BUS600 ProSem: Chapter 4 - Organizational Behavior

The following tree structures illustrated how a large organizational behavior.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




























